Encountering a “DNS server not responding” error can be one of the most frustrating issues when trying to access the internet. The DNS server acts as a translator between website names and IP addresses, allowing your browser to load pages properly. When it stops responding, your connection can fail, leaving you unable to browse, stream, or work online. Knowing how to fix dns server not responding issues efficiently can save both time and stress.
This error can affect computers, laptops, mobile devices, or even your home WiFi network. Users often experience sudden interruptions with no obvious cause. However, by understanding the reasons behind DNS failures and applying proven fixes, most issues can be resolved quickly. From simple restarts to advanced network configuration adjustments, this guide covers all essential steps to restore stable internet access.
What causes a DNS server not responding error?
There are multiple reasons why a DNS server may stop responding. On computers, outdated network drivers or corrupted system files can disrupt DNS communication. Misconfigured DNS settings, firewall restrictions, and antivirus interference are also common culprits. Meanwhile, router glitches, outdated firmware, or even temporary ISP issues can affect all devices connected to your network.
Another frequent cause involves network configuration conflicts. Problems with IPv6 settings, TCP/IP stack errors, or cached DNS entries can prevent your system from connecting to the server correctly. Identifying the exact cause is crucial when learning how to fix dns server not responding, as it ensures you choose the most effective solution for your situation.
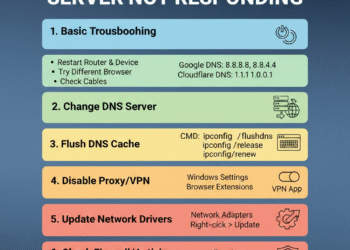
Quick fixes you can try immediately
Restarting your router and computer is often the most effective first step. Powering off your router for 30–60 seconds and restarting your device clears temporary glitches that may be blocking DNS communication. This simple action resolves many connectivity issues without the need for complex adjustments.
Flushing the DNS cache is another quick method to restore proper network function. On Windows, open Command Prompt as an administrator and type ipconfig /flushdns. Mac users can open Terminal and use dscacheutil -flushcache. This process clears outdated or corrupted entries, forcing your system to retrieve fresh DNS information and often fixing errors almost instantly.
Switching to public DNS servers is a reliable approach when default servers fail. Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) and Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) are fast, secure options. Adjusting your DNS settings on a computer or directly through your router can improve connectivity and is an essential step when learning how to fix dns server not responding for persistent network issues.
Advanced fixes for persistent DNS problems
Updating your network adapter drivers ensures your device communicates efficiently with DNS servers. Outdated or corrupted drivers can block connections, leading to the DNS error. Download the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website and follow installation instructions carefully for the best results.
Disabling IPv6 can also help in some cases. Conflicts between IPv6 and IPv4 connections may interfere with DNS requests, causing repeated errors. Access your network adapter settings, uncheck IPv6, and reconnect to your network. Resetting the TCP/IP stack with Windows commands like netsh winsock reset and netsh int ip reset can further repair connectivity problems and restore smooth operation.
Temporarily disabling antivirus or firewall software can reveal whether security programs are blocking DNS communication. While testing, ensure you only disable protections briefly and re-enable them afterwards. Many DNS issues arise due to firewall restrictions or third-party software conflicts, so this step is a valuable part of troubleshooting how to fix dns server not responding effectively.
Device-specific fixes
Windows 10 and 11 users can troubleshoot by changing DNS addresses, flushing caches, and updating drivers through network settings. Mac users can manage DNS under System Preferences and use Terminal to refresh cache. Mobile devices, including Android and iOS, allow DNS adjustments in WiFi settings. Following device-specific instructions ensures that DNS errors are fixed without affecting other network settings.
WiFi and Ethernet connections may also behave differently when resolving DNS issues. Ethernet often requires manual configuration, while WiFi benefits from router-level adjustments. Knowing the differences between connection types is essential when troubleshooting how to fix dns server not responding across multiple devices to guarantee consistent internet access at home or in the office.
Tips to prevent DNS server errors in the future
Preventing DNS issues is easier than dealing with them repeatedly. Keeping network drivers and router firmware updated helps maintain smooth communication between devices and DNS servers. Regularly clearing your DNS cache and using reliable public servers like Google or Cloudflare reduces the chances of encountering errors.
Avoiding unnecessary VPN or firewall conflicts is another key measure. Scheduled system updates and occasional network checks can ensure your devices maintain proper DNS functionality. Following these preventive steps will help reduce interruptions and provide a stable internet experience while also making future troubleshooting faster and simpler.
When to contact your ISP or IT support
If DNS problems persist despite trying all recommended fixes, it may indicate an issue with your ISP or network hardware. Contact your provider to check for outages, server problems, or account-related restrictions. Documenting steps already taken allows technical support to diagnose and resolve the problem efficiently.
Persistent errors that affect multiple devices may also require professional assistance. IT support can assist with router configurations, advanced network settings, or hardware replacement. Knowing when to escalate the issue ensures that you maintain reliable internet access while preventing further frustration caused by DNS server errors.
Conclusion
Knowing how to fix dns server not responding is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted internet access. From quick fixes like restarting routers and flushing caches to advanced solutions such as updating drivers, disabling IPv6, and switching DNS servers, most issues can be resolved at home. Implementing preventive measures and following troubleshooting steps ensures smoother connectivity and a reliable online experience for both personal and professional use.